Introduction
In the vibrant world of superfoods, beets have emerged as unsung heroes. Their deep purple hue and earthy sweetness not only add color and flavor to our plates but also bring a host of health benefits, particularly in the realm of heart health and blood pressure management.
But what’s the real story behind beets and blood pressure? Are all forms of beets equally beneficial? And, if you’re watching your sodium intake or managing diabetes, should you still be reaching for that jar of pickled beets?
In this comprehensive guide, we delve deep into the heart of beets – from their nutritional makeup to their various forms – and unravel the truth about their impact on blood pressure. Whether you’re a beet enthusiast, a health-conscious individual, or simply curious about this root vegetable’s powers, this post is tailored to provide you with practical, useful insights.
Join us as we explore the beetroot’s journey from garden to table and its role in keeping our hearts beating strong and healthy. Let’s unravel the beet mystery together!
Section 1: Understanding Beets
Beets are more than just a vibrant addition to your salad; they are a powerhouse of nutrition. This root vegetable comes in various forms – raw, cooked, pickled, and canned – each offering unique benefits and flavors.
Nutritional Profile of Beets
Beets are low in calories but high in valuable vitamins and minerals. They are rich in fiber, which aids digestion, and packed with essential nutrients like folate, manganese, potassium, and vitamin C. This nutritional profile makes beets a great choice for overall health.
The Heart of the Matter
One of the most remarkable aspects of beets is their high nitrate content. These nitrates are converted into nitric oxide in the body, a compound that relaxes and dilates blood vessels. This process can lead to lower blood pressure and improved heart health.
Beets in Various Forms
- Raw Beets: When eaten raw, beets retain all of their nutrients without any loss due to cooking. They are great in salads or as a crunchy snack.
- Cooked Beets: Cooking beets brings out their natural sweetness and makes them more palatable for some. They can be roasted, boiled, or steamed.
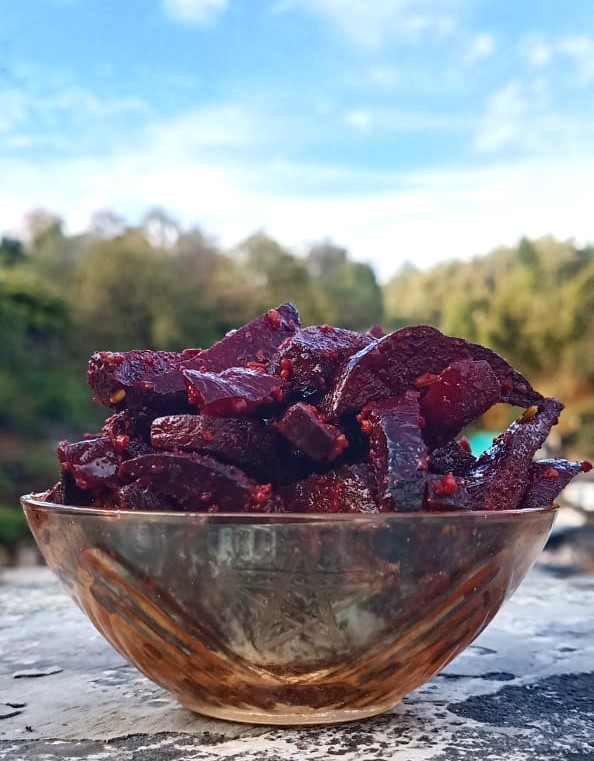
- Pickled Beets: Pickling beets adds a tangy flavor but can also introduce additional sodium and sugar.
- Canned Beets: Convenient and ready to eat, canned beets can be a good alternative. However, check for added sodium and sugars.
Section 2: Beets and Blood Pressure
The link between beets and blood pressure is a topic of much interest and research. The key lies in the beetroot’s natural nitrates, which have a direct impact on blood vessel health and blood pressure regulation.
How Beets Affect Blood Pressure
The nitrates in beets are converted into nitric oxide, a molecule that plays a crucial role in dilating blood vessels. This dilation can lead to a reduction in blood pressure, making beets a natural ally for those looking to manage hypertension.
The Research Says
Studies have shown that regular consumption of beetroot juice can significantly lower blood pressure in individuals with hypertension. It’s believed that the effects are most pronounced within a few hours of consumption and can last up to 24 hours.
Section 3: The Pickled Beets Perspective
Pickled beets are a popular form of this vegetable, but their impact on blood pressure is a bit more complex.
Benefits and Downsides
While pickled beets retain the blood pressure-lowering nitrates, the pickling process often introduces high levels of sodium, which can counteract these benefits. For those with hypertension, this high sodium content can be a concern.
Moderation is Key
Enjoying pickled beets in moderation, as part of a balanced diet, can help you reap their benefits without overdoing the sodium. It’s also a good idea to look for low-sodium varieties or consider making your own pickled beets at home with less salt.
Section 4: Beets for Diabetics
Navigating the world of nutrition can be particularly challenging for diabetics, and beets, especially in their pickled form, warrant a closer look.
The Sugar Content in Beets
Beets naturally contain sugars, which raise concerns for individuals monitoring their blood sugar levels. However, the fiber content in beets can help balance this out, leading to a more gradual increase in blood sugar rather than a spike.
Pickled Beets: A Double-Edged Sword
While pickled beets maintain most of the nutritional benefits of raw beets, the added sugars in the pickling process can be a red flag for diabetics. It’s essential to check the label for added sugars and consider portion control.
Alternatives for Diabetics
For diabetics looking to enjoy the benefits of beets without the added sugar, raw or lightly cooked beets can be a better choice. These forms offer the nutritional advantages without the added sugars found in some pickled or canned varieties.
Section 5: Comparing Beet Forms
Understanding the different forms of beets and their respective impacts on health is crucial for making informed dietary choices.
Raw vs Cooked Beets
While raw beets retain all their nutrients, cooking can enhance their taste and make them more digestible. Both forms provide heart-healthy benefits, but raw beets might have a slight edge in terms of nutrient preservation.
Pickled vs Canned Beets
Pickled beets offer a unique flavor and are convenient, but their high sodium and potential sugar content can be drawbacks. Canned beets are a practical alternative, but it’s important to choose varieties without added sodium or sugars.
The Best Way to Consume Beets for Blood Pressure
For those specifically looking to manage blood pressure, consuming beets in their raw or lightly cooked form is recommended. This ensures the maximum intake of nitrates without the added sodium or sugars.
Section 6: Dietary Recommendations
Incorporating beets into your diet can be beneficial, but it’s important to do so in a balanced and informed way.
The Right Amount
A serving size of about half a cup of beets is sufficient to reap the health benefits without overindulging in natural sugars or potential sodium in pickled or canned forms.
Creative Ways to Include Beets in Your Diet
- Add grated raw beets to salads for a nutritious crunch.
- Blend cooked beets into smoothies for a nutrient-rich drink.
- Use pickled beets as a tangy addition to sandwiches or wraps, in moderation.
- Roast beets with a drizzle of olive oil and herbs for a heart-healthy side dish.
Section 7: FAQs Answered
In this section, we’ll address the common queries about beets and blood pressure, offering clear and concise answers.
1. Do Pickled Beets Lower Blood Pressure?
While pickled beets contain blood pressure-lowering nitrates, their high sodium content can counteract these benefits. They can be a part of a blood pressure-friendly diet if consumed in moderation and if low-sodium options are chosen.
2. Can Pickled Beets Lower Blood Pressure?
Yes, the nitrates in pickled beets can help lower blood pressure. However, be mindful of the sodium content, as excessive sodium can increase blood pressure.
3. Are Pickled Beets Good for Diabetics?
Pickled beets, due to added sugars, might not be the best option for diabetics. It’s better to opt for fresh or cooked beets with no added sugars.
4. Pickled Beets for Blood Pressure: Good or Bad?
Pickled beets can be beneficial due to their nitrate content, but their sodium levels make them a less optimal choice for blood pressure management compared to other forms of beets.
5. Canned Beets and Blood Pressure: What’s the Verdict?
Canned beets can be a convenient option, but like pickled beets, watch out for added sodium and sugars. Always check labels and opt for low-sodium, no-added-sugar varieties.
6. Are Pickled Beets as Nutritious as Raw Beets?
Pickled beets retain most nutrients but also have added sodium and sugars. Raw beets provide the most natural nutrients without these additions.
7. Does the Form of Beet Matter for High Blood Pressure?
Yes, the form of beet can matter. Raw or lightly cooked beets are the best choices for high blood pressure due to their high nitrate and low sodium content.
Conclusion
Beets, in their various forms, offer a spectrum of nutritional benefits, particularly in the realm of heart health and blood pressure management. However, understanding their different forms and the specific health considerations associated with each is crucial for maximizing these benefits. While raw and cooked beets are generally the best choices for blood pressure management, pickled and canned beets can still be included in a balanced diet with careful consideration of their sodium and sugar content.
Remember, the key is balance and moderation. Beets can be a wonderful addition to your diet, but they are most beneficial when part of a diverse and balanced dietary pattern.
Call to Action
We’d love to hear your thoughts and experiences with beets! Do you have any favorite recipes or tips for including beets in your diet? Share them in the comments below. And as always, for personalized dietary advice, especially if you have specific health concerns, consulting a healthcare professional is recommended.